What is Cloud Hosting?
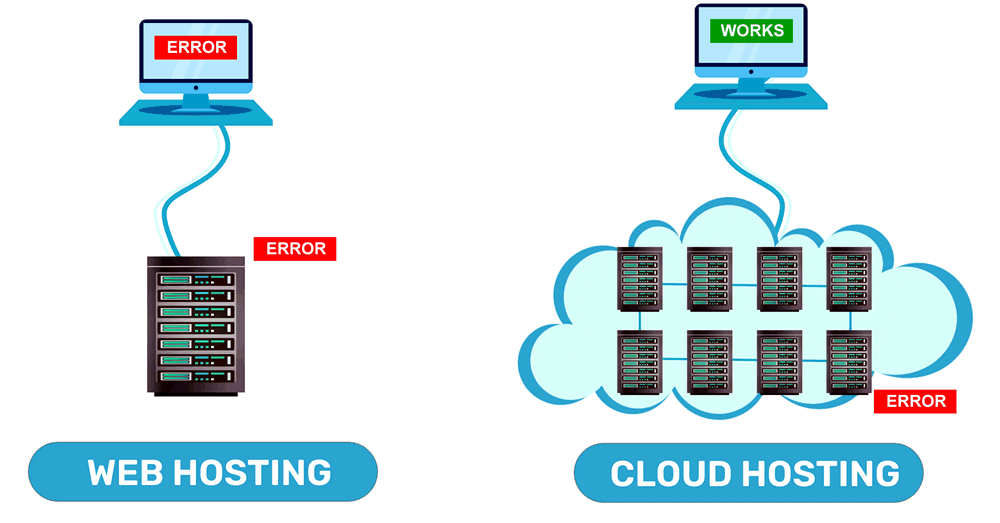
Cloud hosting, also known as a cloud server, is a type of web hosting that leverages the resources of several virtual servers to distribute and balance the demand, allowing a web page to remain online without experiencing crashes or other difficulties. Difficulties that may affect the processing speed at which data is sent from it
The fact that this type of hosting does not overload, as well as the possibility that, if given the case, we receive more visits than expected on our website, a whole slew of additional resources will be used to successfully solve this situation (this is called scalability, a concept that we will see later), make cloud hosting the most viable option.
Who uses cloud hosting?
There are instances where using this form of hosting is quite convenient, such as in an online store, lead generating sites, corporate websites, news agencies, publishers, and other sites with large traffic, such as the great majority of social networks.
Types of cloud hosting
We have numerous types of cloud hosting at our disposal, including public, private, hybrid, and managed cloud hosting, and we can choose the one that best meets our demands and requirements.
Public cloud hosting
Hosting in the public cloud is intended for “external” customers or users, that is, those who would use it as a service, using the same provider’s resources and infrastructure, however, they will be segregated from other users in terms of security and privacy.
Each client can lease a set number of these resources, and the fee will be proportionate to the number of them used, with the option to increase it automatically at a certain time if necessary. This is referred to as scalability.
The benefit of choosing this kind of hosting is that the platform will be maintained and handled by the provider, leaving us with simply the administration of our site and a slew of tools that it will make available to us.

Private cloud hosting
The Private Cloud, on the other hand, provides the same service to a smaller and more particular group of users who will have exclusive access to the resources they have contracted, i.e. they will have them totally at their disposal.
When a company, for example, employs dedicated servers and runs its private cloud on them, the company owns the cloud infrastructure. As a result, administration, configuration, and installation will be entirely up to the owner.
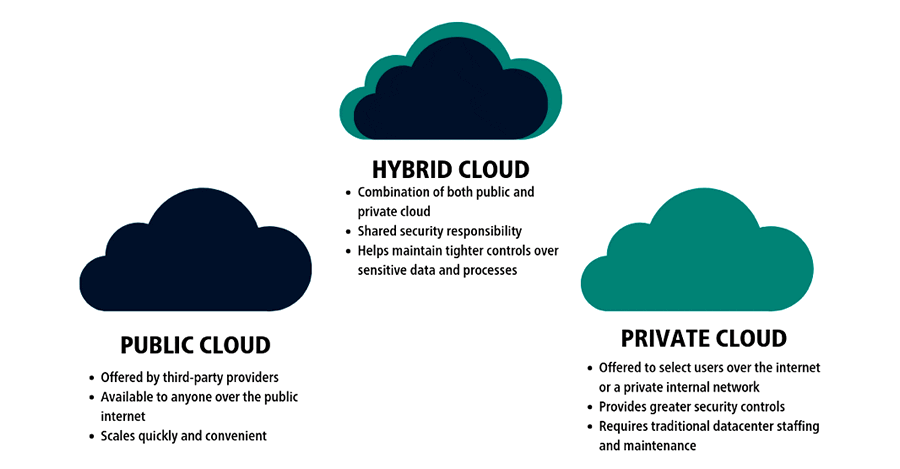
Hybrid cloud hosting
Hybrid cloud hosting is a blend of private and public cloud hosting. Whereas public clouds often charge for the resources utilized by the site, a private cloud is far more cost-effective because the entire server is hired.
We will save money by using both at the same time, and we will be able to build new instances within a public hosting service based on our needs, rather than having to acquire and set up extra servers, as would be the case with an exclusive private one.
Managed cloud hosting
The only thing we’ll have to do with this form of hosting is telling the provider what we’ll be hosting on the server and what our resource requirements are.
The cloud hosting administrator will be responsible for the server’s configuration and maintenance, as well as the procurement of licenses and the installation of apps.
What factors should you consider while selecting a Cloud Hosting service?

It is critical to understand what aspects we must consider when selecting one cloud hosting company over another based on our demands.
These elements are:
Scalability and adaptability
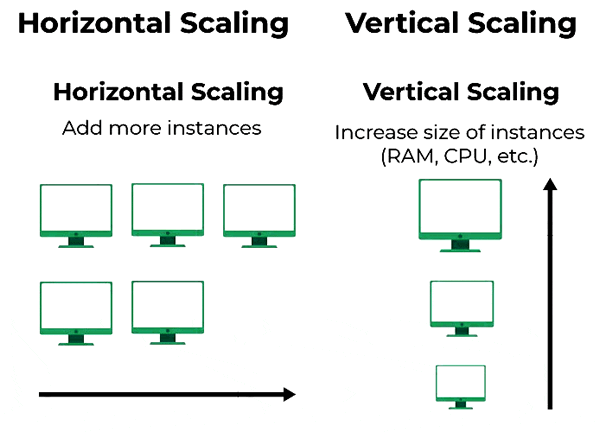
Scalability is the ability to increase or reduce the resources used by the site based on the demand for utilization at any one time, giving us some flexibility in how we use them depending on what our site may require.
This availability based on requirements is highly intriguing for certain sites, as there will be moments when the peak of activity grows significantly, and others when it does not.
CPUs
We must also consider the processing capacity that we wish to obtain, as this will have a significant impact on the site’s loading speed. As we have seen in the previous point, if we contract a cloud hosting in which we can have scalability, we will be able to increase the processing capacity at specific times, so a priori, if we take into account what we will need in normal circumstances, we will not have a problem if at specific times we require an extra.

Memory
The RAM memory capacity that we get is also an important factor in ensuring that our site runs swiftly and efficiently.
Storage
The amount of storage that our site requires will be determined by the pieces that comprise it as well as the type of service that we provide. It will also be vital to consider the administrative aspect of the site, as well as how much space our website takes up.
IP On Demand
It is also critical to consider the sort of IP we will obtain: It will be shared in a public cloud hosting environment, but exclusive in a private or hybrid cloud hosting environment.

Location
Although the location may not be a concern for very tiny sites, it can have an impact on us and even our clients.
If the servers that host our website are located in a remote location, we will begin to notice issues such as high latency and poor website performance as our requirements grow.
As a result, we must assess whether our site will require a server with geolocation close to ours, or whether it will not.
Redundancy is a solution to this problem that is now commonly offered in most cloud hosting services:
Redundancy
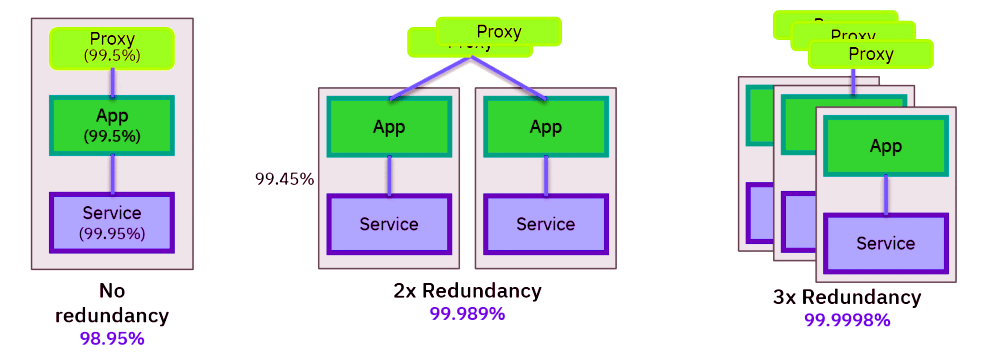
It is a process by which all the files or packages are stored in a network of servers that are located in different parts of the world so that all the information related to our website will be copied in at least two places at the same time.
In addition to assuming a solution to possible data protection and privacy problems, the server that will send us the content will be the one that is closest, depending on where our geographical location is.
Redundancy is not a novel concept; it has been in use for many years. Traditionally, redundancy was achieved by having a mirror hard drive that simultaneously replicated all of the contents of another hard disc. As a result, if the main drive failed, you always had a complete copy of the data on the backup disc. These entire clones of servers are now referred to as clusters.
Support
When deciding between two options, we must consider the support that the provider provides in the event of an issue.
Normally, they all offer the ability to reach them at any time of day, 365 days a year. However, we should carry out a thorough investigation, find out, for example, how long they take to respond, and if other clients have had any problems in this regard.



