Many businesses and e-commerce websites choose private environments with dedicated resources when it comes to hosting their websites – after all, their online presence is their bread and butter! They just cannot risk not having enough resources to handle the volume of traffic and usage that they are seeing. Their money and revenues are dependent upon it.
As a result, virtual private server hosting is becoming more popular among businesses. When compared to dedicated servers, virtual private server (VPS) hosting is an excellent mid-level web hosting platform that is not nearly as expensive or time-consuming to run as dedicated servers but provides significantly more capacity and scalability than shared hosting. VPS hosting is incredibly trustworthy and resource-rich, and it is typically favored over its more expensive dedicated counterpart due to its lower cost.
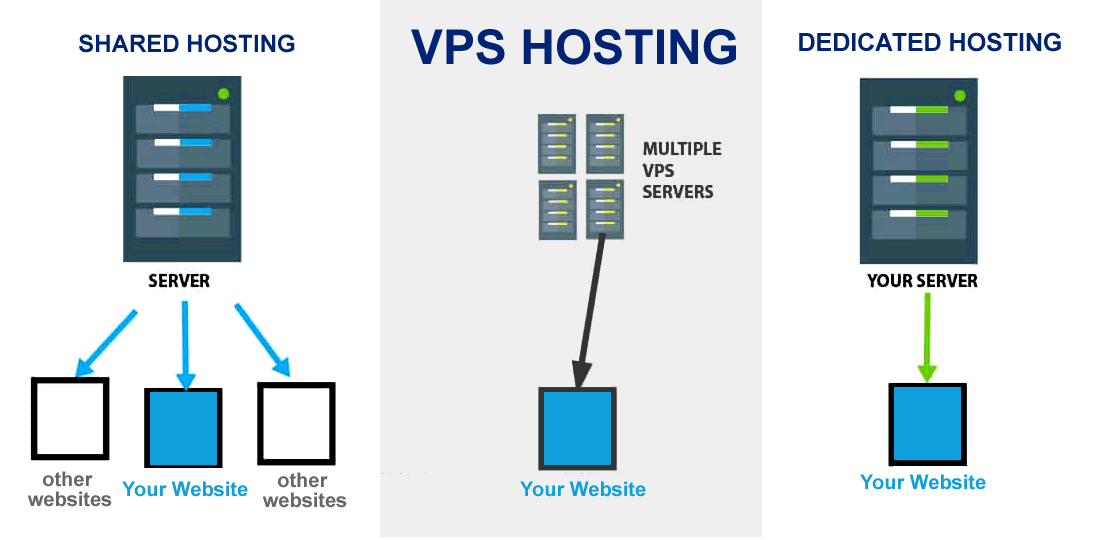
What is a VPS?
So, what exactly is a virtual private server?
A virtual private server (also known as a VPS) is a virtual server that is installed on a computer and is capable of operating many websites concurrently. A computer can host multiple virtual private servers, each of which runs a separate operating system (the most common of which are Windows and Linux, which we shall examine later in this post) and is dedicated to hosting content for a single user. Virtual private servers (VPS) are designed to execute the server software and applications required by individual clients and are tailored to their specific needs.
Because it is a customized and completely isolated environment, you can reboot independently at any moment. The ability to run virtual private servers with their own root-level privileges, memory, apps, configuration files (and more!) – is one of the greatest advantages of using them. Shared hosting doesn’t even come close to the level of freedom that you have with VPS.
A virtual private server (VPS) is an ideal alternative for you as long as your website and the apps you run do not have exorbitant resource requirements.
If you’re not sure whether your company should go with the simpler and less expensive shared hosting environments or the more robust and sophisticated virtual private server options, then you will need to get to know more about them in detail and find for yourself which one suits you best.
Linux VPS or Windows VPS?

After determining that a virtual private server (VPS) is the best option for you and your website, the following step is to select the operating system (OS) to operate on the server.
You can pick between a Linux-based server and a Windows-based server when using a virtual private server. Although the two operating systems share many essential features, there are major differences, and the operating system that is chosen will be determined by the particular user and their preferences. So, let’s take a look at the differences between the two solutions to help you determine which one to go with.
Cost
The cost of the two services is the most obvious distinction between them straight out of the gate.
Linux is a free and open-source operating system, whereas Windows is a commercial operating system that must be purchased. As a result, both the type of usage and the pricing of Windows and Linux virtual private servers fluctuate significantly.
When it comes to Windows, license rates must be considered. Additionally, because Windows VPS servers may be subject to more specialized responsibilities, they are more expensive than typical shared hosting plans.
If you have a restricted budget and no demanding specifications or functional needs, Linux virtual private servers (VPS) are a good option. In general, a Linux virtual private server (VPS) with the same specifications is less expensive than a Windows virtual private server with the same specifications.

Tech Considerations
The technology stack on which your website and business are created is the second most important factor to consider.
Obviously, if you’re working with conventional Active Server Pages (ASP) you’ll want to take advantage of the excellent integration for these programming scripts that a Windows VPS environment can provide. If you have a Microsoft SQL database, the same is true; in this situation, selecting a Microsoft Windows-based hosting product makes the most sense. Windows Virtual Private Servers (VPS) are designed for businesses that rely on Microsoft software, and they offer a greater range of support as well as more frequent and smoother updates than other types of servers.
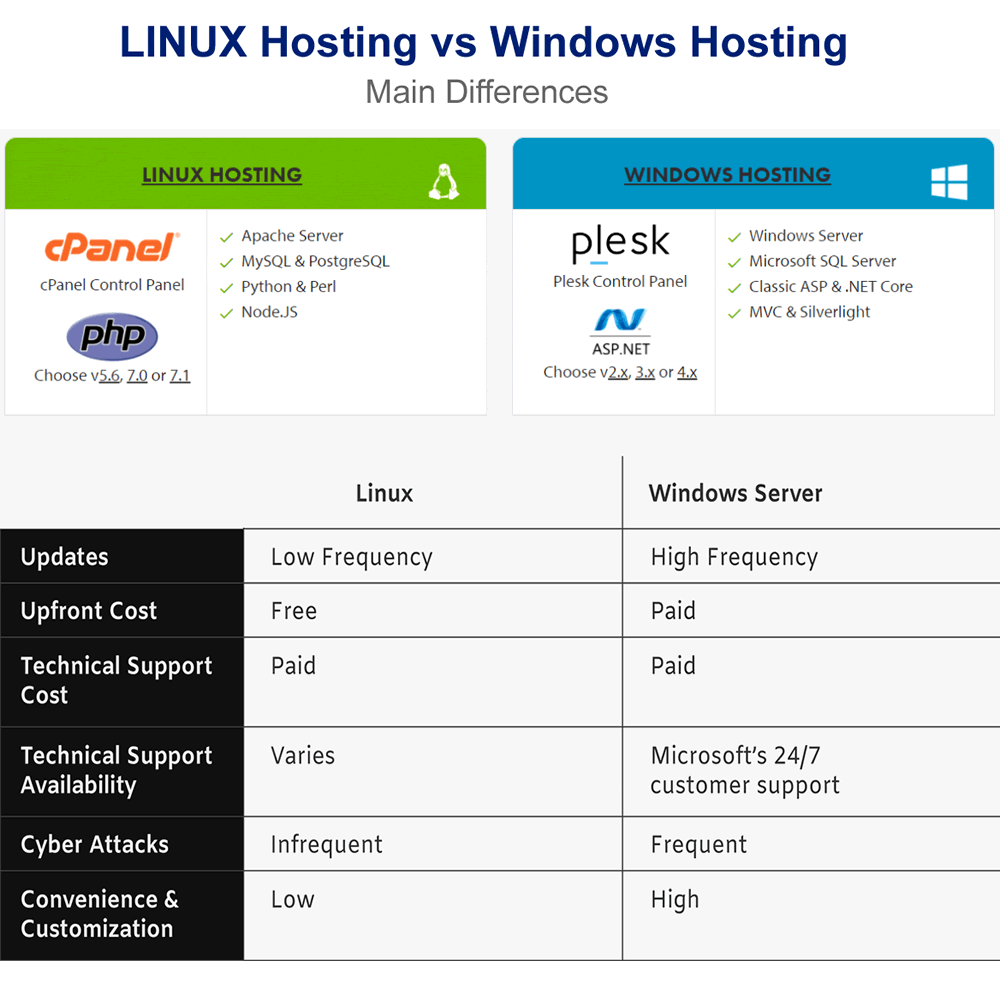
If, on the other hand, you wish to use open-source software for development, such as PHP, or MySQL for your database, a Linux virtual private server (VPS) is a great option. There are numerous Linux distribution choices available, including CentOS, Debian, and Ubuntu, to mention a few.
Ease of Use
If you are a beginner or do not have a seasoned IT team on your side, a Windows VPS can be easier to manage due to its remote desktop with direct GUI access and virtualization features.
A Linux virtual private server, on the other hand, is maintained via SSH, requiring a greater level of technical expertise and skill to ensure that everything is properly configured and running. Nonetheless, if you or your team have this knowledge, Linux is a very effective operating system for managing your server. Many people with technical skills believe that Linux is more user-friendly when it comes to executing specific tasks and controlling their surroundings.
A Quick Comparison between Windows vs Linux VPS
To summarise, the following are the main differences between the two operating systems.
Windows VPS
- Higher price tag
- More regular updates
- Broader support base
- Accommodates more demanding requirements

Linux VPS
- Open-source
- Budget-friendly
- Good for simpler requirements
- Requires more technical knowledge

There are many hosting providers that offer Virtual Private Servers (VPS) in both Windows and Linux flavors, with dedicated and scalable resources, as well as the award-winning Parallels Plesk Panel. Your VPS will have its own operating system with its own web server, FTP server, mail server, hosting control panel, and other applications, regardless of which operating system you choose. You can have the independence you desire at a cost that is within your means.
It all comes down to your company’s specific needs when determining whether to employ a Windows or a Linux virtual private server.
Do you have any more questions? Let us know in the comments section.



